| |
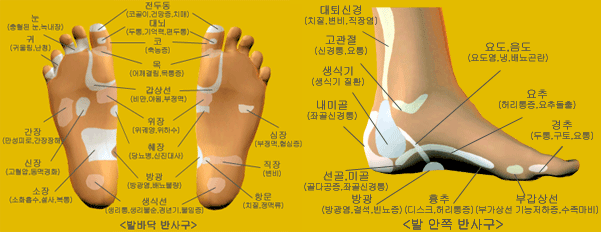 |
Each foot represents half of the body, the left and right foot corresponding to the left and right side of the body. Here is a list of the divisions of the feet and the areas of the body to which they correspond:
TOES = Head and neckBALLS OF FEET (METATARSALS) = Chest, lung area, shoulderARCH (UPPER PART) =
Diaphragm to waist area, upper abdominal organsARCH (LOWER PART) = Waist to pelvic area, lower abdominal
organsHEEL = Pelvic area/sciatic nerveINNER FOOT (MEDIAL SIDE) = SpineOUTER FOOT (LATERAL SIDE) =
Arm, shoulder, hip, leg, knee, lower backANKLE AREA = Pelvic area, reproductive organs
Using these divisions and the five zones, you can locate any area of the body on the mini-map of the foot. Let's
say someone indicatesa pain by pointing to the area just beneath the rib cage on the right and a little above
the waist. Without knowing exactly what the problem is, you can locate the specific area on the foot. Since
the pain is on the right, the reflex point would be on theright foot between the diaphragm line and the waist
line and along zone 5. A reflex point is a specific area or point on the foot that corresponds to another part of
the body. When stimulated by the thumbs or fingers, there is a response to the stimulus in another part of the
body.
You will also notice another guideline for locating specific points on the foot. This is the long tendon that runs
vertically down the arch between zones 1 and 2. To find the tendon, pull the toes back to stretch the skin
tighter across the arch.
The tendon will come forward. It is important not to apply pressure on the tendon itself when you are working
this area, because doing so is painful.
Always hop over the tendon when you are thumb walking in this area. As you become better acquainted with
the foot, you'll begin to think of certain points as being either to the left or right of this tendon.
Now let's take a closer look at each section of the foot and the specific gland, organ, and body part to which
each refers.
1. THE TOES
The toes correspond to the head and the neck. Specifically, each big toe is the "master toe" for that side of the body because all five zones which run down that side of the body converge in this toe. Each big toe contains reflex points for the pituitary, pineal, hypothalamus, brain, temples, upper and lower jaw,
gums, teeth, throat, thyroid/parathyroid, and the seven cervical (neck) vertebra.
 Pituitary Pituitary
Considered the master gland, the pituitary is located at the base of the brain and directly secretes or controls the secretion of almost every hormone in the body. The pituitary, affects growth, sexual development, fever, fainting, pregnancy, lactation, metabolism, mineral and sugar contents of the blood,
fluid retention, and energy levels -- to name just a few of its activities. Its reflex point is the center of
the big toe on both feet.
 Pineal Pineal
A poorly understood gland in the brain that responds to levels of daylight perceived through the eye with release of the hormone melatonin. The pineal is thoughtto play a part in mood and circadian rhythms. It is
often referred to as our intuitive gland or "third eve." Its reflex point is located in zone 1,
at the inner side and top of the big toe on both feet.
 Hypothalamus Hypothalamus
This gland regulates the autonomic nervous system and controls emotional reactions, appetite, and body
temperature. It has the same reflex point as the pineal.
 Thyroid Thyroid
Located in the neck, the thyroid controls metabolism. Its hormones regulate protein building by the body's
cells, the rate at which nutrients are used by the body, and calcium levels.
Metabolism affects the pace of our lives and our energy levels.
The thyroid's reflex area is at the base of the big toe on both feet.
 Parathyroids Parathyroids
Situated around the thyroid, the parathyroid glands affect calcium and phosphorus levels,
which are important for muscle tone and functioning.
 Seven Cervicals Seven Cervicals
The seventh cervical vertebra is the last vertebra in the neck.
It protrudes at the base of the neck and can be easily felt. Many of the nerves of the arm and hand and the
muscles of the neck pass by the seventh cervical vertebra. Its reflex point is located at the base of the
big toe on the medial side of both feet in zone 1. The reflex points of cervicals 1 to 6 run from the base of
the toenail to the seventh cervical, zone 1.
The small toes each contain one zone and are used for fine-tuning for head and neck ailments,
such as sinusitis, eyestrain, hearing problems, jaw problems, and neck tension. The tips of all the
toes should be worked for people with head or brain injuries and strokes.
The ridge at the base of the toes (actually on the ball of the foot) is worked as a helper reflex area for eye,
ear, and eustachian tube disorders. This ridge corresponds to the neck/shoulder line;
it is here that many people hold tension that can block circulation to the head.
2. THE BALL OF THE FOOT
The ball of the foot corresponds to the area of the body between the diaphragm and neck.
Here are several vital reflex areas, including those for the heart and lungs.
 Heart and Lungs Heart and Lungs
The lungsare light and spongy organs in the chest where the actual exchange of new,
oxygenated air and used, deoxygenated air takes place. The heart is a hollow muscle which rhythmically
contracts to pump the blood through the vessels in all parts of the body. Its reflex areas are on the left foot,
zones 1 to 4, and on the right foot, zones 1 and 2. The chest area also contains other important structures,
such as the major vessels leading to and from the heart (venae cavae, aorta), the tubes of the respiratory,
and digestive system (trachea and esophagus), and the nerve which controls the diaphragm.
 Solar Plexus Solar Plexus
Another important structure in this region is the solar plexus,or the network of nerves in the autonomic
(or involuntary) nervous system which regulates the functioning of the organs.
The solar plexus is located between zones 2 and 3 on both feet beneath the diaphragm line.
 Lymph System Lymph System
On the front of the foot, between the first and second toes, is the reflex area for the drainage of the
lymphatics in the neck/chest region of the body. The lymph system parallels the network of veins in the
body, and serves two important functions: to remove large proteins from the tissue and return them to
circulation for eventual elimination, and to produce the cells which defend the body from foreign
bacteria and viruses. The lymph system also removes excess fluid which has accumulated in tissue
spaces.
3. THE ARCH AND HEEL
The arch of the foot is divided into two parts. The upper part corresponds to the area from the diaphragm
down to the waistline. The lower part corresponds to the body from the waistline to the pelvic line.
The upper part of the arch contains reflex areas for the liver and gallbladder, stomach, pancreas,
duodenum, spleen, adrenals, and top part of the kidneys.
 Liver Liver
The liver is the largest organ and gland in the body, located beneath the diaphragm under the rib cage
mostly on the right side. Its reflex area is on the right foot, zones 1 to 5, between the diaphragm line and
the waist line. The liver processes all the nutrients from the blood, storing fats, sugars, and proteins until
the body needs them. It detoxifies the blood and manufactures bile for fat digestion and important blood
proteins. The liver has over 500 functions.
 Gallbladder Gallbladder
Embedded in the liver, the gallbladder stores bile used for breaking down fats. Its reflex point is between
zones 4 and 5, about two fingers above the waistline on the right foot.
 Stomach Stomach
The stomach is located mostly on the left side of the body under the diaphragm.
It churns food and begins protein breakdown. Its reflex area is found mostly on the left foot, zones 1 to 4,
and on the right foot in zones 1 to 2.
 Pancreas Pancreas
The pancreas is behind the stomach, mostly on the left side of the body. Its reflex area is located mostly
on the left foot, zones 1 to 4, and a little on the right, zones 1 to 1 1/2. The pancreas controls glucose
levels in the blood and is involved in the building of proteins by the cells. The pancreas also sends
important digestive enzymes into the small intestine.
 Duodenum Duodenum
The duodenum is the first C-shaped part of the small intestine and is responsible for the breakdown of food.
The average length is about ten inches. It connects the pylorus of the stomach to the jejunum. It receives
hepatic and pancreatic secretions. The reflex area to the duodenum is located on both feet, zone 1,
medial to the tendon, on the waistline.
 Spleen Spleen
The spleen is on the left side of the body under the diaphragm and behind the stomach. Part of the
lymphatic system, it produces lymphocytes and stores or filters out old and damaged blood cells.
It filters the lymph of toxins and bacteria, and produces antibodies. It is an important part of our immune
system. Its reflex point is found on the left foot between zones 4 and 5, about two finger widths above
the waist line.
 Adrenals Adrenals
The adrenal glands sit on top of the kidneys and have over fifty functions. Their reflex points are on both feet midway between the diaphragm line and waistline, in zone 1. The adrenals promote normal metabolism by controlling energy levels -- especially by increasing energy, in response to stress. The adrenals produce cortisone and cortisol, which have anti-inflammatory properties. The adrenals may be involved in sexual development. To a large extent, the adrenals are responsible for the organ changes in fight-or-flight reactions to stress, including increased heart rate, vasoconstriction, increased breathing rate, increased efficiency of muscle contractions, and improved balance of metabolism.
The lower part of the arch contains reflex areas and points for the kidneys, ureters, bladder, small intestines, appendix, ileocecal valve, and colon.
 Kidneys Kidneys
The kidneys, in the mid-back area, are the master filters of the body. They filter toxins from the blood and produce urine. They also regulate retention of important minerals and water. Their reflex areas are found on both feet in zone 3, on the waist line.
 Ureters Ureters
These tubes connecting the kidneys and bladder are passageways for urine. Their reflex areas are on both feet, in zone 1, between the pelvic and waist lines.
 Bladder Bladder
The bladder, in the center of the lower abdomen, is a storage place for urine. Its reflex area is at the heel line on both feet, zone 1.
 Small Intestine Small Intestine
The small intestine secretes some digestive juices and absorbs digested foods, water, vitamins, and minerals. Its reflex area is found on both feet from the waist line to the pelvic line inside the large intestine area, zones 1 to 4.
 Ileocecal Valve Ileocecal Valve
The ileocecal valve lies between the small and large intestines, prevents backflow of fecal matter from large to small intestine, and controls mucous secretion. Its reflex point is found on the right foot in zone 5, about two finger widths below the waist line.
 Colon Colon
The colon ascends from the ileocecal valve, between zones 4 and 5, turns under the liver, crosses over at the waist line, and turns down under the spleen, to become the sigmoid colon. It absorbs water, and stores and eliminates mucus and waste material.
 Appendix Appendix
The appendix, located at the beginning of the colon, lubricates the large intestine, and may secrete antibodies. Its reflex point is located on the right foot, zone 5, two finger widths below the waist line (same place as ileocecal valve).
 Sigmoid Colon Sigmoid Colon
This S-shaped section of the colon is the last intestinal turn before the body wastes empty into the rectum for elimination. Gas can become trapped here. Its reflex point is on the left foot, in zone 3 1/2 at the middle of the heel
 Sciatic Nerve Sciatic Nerve
Beneath the sigmoid colon and on both heels is the sciatic nerve. This is the only area that is not a reflex area but an actual nerve, running from the base of the heel up the leg and into the buttocks.
4.THE INNER FOOT
 Spine Spine
Look down at your feet, and notice that the inside of each foot is naturally curved to correspond to the spine. In zone 1, the area from the base of the big toenail to the base of the toe, corresponds to the cervical vertebrae found in the neck. The large bulge beneath the big toe corresponds to the thoracic section of the spine (shoulders to waistline). The indentation between the middle of the foot and the heel (waist line to pelvic line) corresponds to the lumbar region. The area from the heel line to the base of the heel corresponds to the sacrum/coccyx, the very base of the spine. The reflex area for the bladder is found just below the lumbar region on the inside of each foot.
 Thymus Thymus
The thymus is a lymphatic organ located in front of and above the heart. Its primary function is to develop immunity, in children. On the foot, the thymus gland is located in zone 1, along the reflex to the spine, in the neck area.
5. THE OUTER FOOT
Looking down at your feet, you can see that the outer edge of zone 5 corresponds to the outer part of the body: shoulder and upper arm (base of toe to diaphragm line); elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand (diaphragm line to waist line); leg, knee, and hip (from the fifthmetatarsal to the heel line). The metatarsals are the bones that run from the base of the toes down the foot to the waist line. The fifth metatarsal is easily found by running your finger down the outside of the foot to where you feel a bone sticking out on zone 5 -- on the outside edge of the foot at the waist line.
6. ANKLE AREA
The area around each ankle on each foot corresponds to the pelvic area and reproductive organs. The outer ankle area contains the ovary/testicle reflex points; the inner ankle contains reflex points for the uterus/prostate, vagina, penis,and bladder. Reflex points for the fallopian tubes, lymph drainage area in the groin, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles are found in a narrow band running from below the anklebone across the top of the foot from one anklebone to the other. The general chronic pelvic/rectum/prostate/uterus and sciatic nerve area begins about six inches above the anklebone and runs down to the uterus/prostate point below the ankle.
The sciatic nerve travels down both sides of the leg and across the heel like a stirrup. This is the actual nerve, not a reflex area. Therefore it is usually quite sensitive.
 Ovaries Ovaries
The ovaries lie to the right and left of the uterus and produce ova and female hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, which are responsible for female sexual development. Their reflex points are located on both feet, on the outside of the ankles, midway on a diagonal from the base of the heel to the anklebone.
 Testicles Testicles
These are the two glands in the scrotum that produce sperm and the male hormone testosterone. Their reflex points are found on both feet on the outside of the ankles, midway on a diagonal from the base of the heel to the anklebone.
 Prostate Prostate
This gland surrounds the neck of the bladder in the male, and secretes the fluid part of the semen. Reflex points are located on both feet, on the inside of the ankles, midway on a diagonal from the base of the heel to the anklebone.
 Uterus Uterus
Located in the mid-pelvic area, the uterus contains and nourishes the fetus during pregnancy. Reflex points are located on both feet on the inside of the ankles, midway on a diagonal from the base of the heel to the anklebone.
 Fallopian Tubes Fallopian Tubes
A pair of tubes that serve as passageways for the egg as it travels from the ovary to the uterus. Reflex areas are located on both feet across the top of the foot from one anklebone to the other.
 Seminal Vesicles/Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles/Vas Deferens
The seminal vesicles are organs lying next to the prostate which store semen. The vas deferens is the tube that carries the sperm from the prostate to the urethra. The reflex areas are located on both feet across the top of the foot from one anklebone to the other.
|